Osteoarthritis of the knee is the most common form of knee arthritis.
 Page updated January 2024 by Dr Sheila Strover (Clinical Editor)
Page updated January 2024 by Dr Sheila Strover (Clinical Editor)

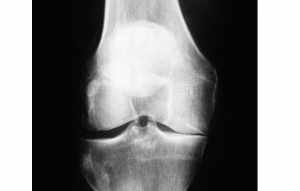
Symptoms of knee osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis begins with breakdown of the joint cartilage at the ends of the bones. Classical symptoms include pain at rest, reduced exercise tolerance, joint swelling and eventual joint deformity.
Diagnosing osteoarthritis of the knee
Usually knee osteoarthritis begins in one part of the knee (what we call a 'compartment'), such as the contact area between femur and tibia on the one side. Only later does it tend to progress to involve the other compartments. This gives the patient the option to try to arrest progression by suitable intervention, such as wearing an unloader brace or having a uni-compartmental knee replacement.
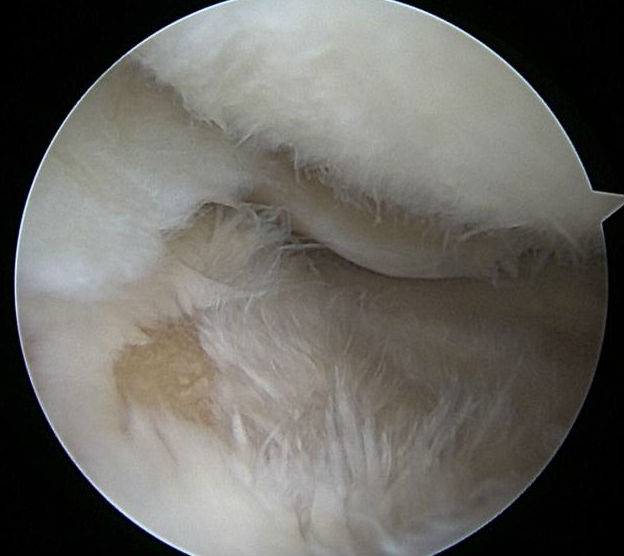
Grade IV damage
Keyhole surgery is not indicated, but if you look inside the joint you would see damage to the usually silky joint cartilage breakdown.
Classical imaging signs include joint line narrowing, bone spurs, bone cysts and areas of increased bone density (sclerosis).
The concept of compartmental arthritis
The bones of the knee actually have three areas of articulation, not one. The two rounded condyles of the femur make articulate separately with the flattened tibia. The kneecap or patella has a third area of articulation with the femur. Each of these is really a separate 'joint', which we call a 'compartment'. Arthritis may initiate at different times in these compartments, depending upon those factors that have triggered it off, such as a damaged meniscus just on the one side.
So it is helpful if the surgeon can intervene and improve function in the one compartment, before the changed mechanics of the knee causes arthritis to affect the other compartments also.
How is knee osteoarthritis managed?
Doctors tend to take different approaches in the management of osteoarthritis depending on their particular line of interest - a general practitioner may tend to look at general factors such as weight and diet, a rheumatologist may prescribe anti-inflammatories, including steroids, and knee surgeons tend to take a mechanical approach and try and sort out any structural problems.
Early osteoarthritis is managed conservatively with anti-inflammatory medications, removal of fluid in the joint and injections into the knee. As deformity progresses, minor procedures might be performed, such as removal of bone spurs, but later deformities may be indications for osteotomy, unicompartmental knee replacement or total knee replacement.
Peer-reviewed papers
-
Quote:
The Clinical diagnosis of knee osteoarthritis is "Knee pain for most days of the prior month, in addition to at least 3 of the following:
- crepitus on active joint motion
- morning stiffness less than 30 minutes’ duration
- age older than 50 years
- bony enlargement of the knee on examination
- bony tenderness of the knee on examination
- no palpable warmth."
Citation: Lespasio MJ, Piuzzi NS, Husni ME, Muschler GF, Guarino A, Mont MA. Knee Osteoarthritis: A Primer. Perm J. 2017;21:16-183. doi: 10.7812/TPP/16-183. PMID: 29035179; PMCID: PMC5638628.
Changes in arthritis -
Concept of compartments -
Arthritis evaluation -
Arthritis interventions -
Surgery for arthritis -
From the Experts -
- Expert view - 2017 - Why do some patients experience osteoarthritis pain before changes are evident on X-ray? - by Dr Lars Blønd (Knee Surgeon)
 2018 -
2018 -