A double-level osteotomy is a procedure where both tibia and femur bones are cut across and realigned in the same procedure. This surgery is relevant in patients who have marked lower limb alignment problems, and involves simultaneous high tibial osteotomy and distal femoral osteotomy.
 Page updated May 2024 by Dr Sheila Strover (Clinical Editor)
Page updated May 2024 by Dr Sheila Strover (Clinical Editor)
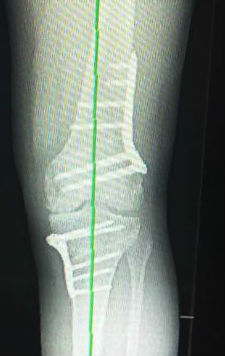
High tibial osteotomy (HTO) for most symptomatic varus patients
Most patients who opt for osteotomy correction of a bow-leg (varus) deformity will be offered a simple high tibial osteotomy.
Adequate digital planning on long leg weight-bearing X-rays will usually guide the surgeon as to the amount of correction that can be safely provided by correction in just the one bone.
Double-level osteotomy for large or complex corrections
If correction is likely to be compromised with a single level osteotomy, then the planning can be revised to calculate what corrections would be needed in both tibia and femur simultaneously to provide adequate safe realignment.
So in these severe cases of bow legs, the surgeon may opt instead for a double-level osteotomy.
-
Quote from peer-reviewed paper:
"....Multiple studies published more than 30 years ago advocated against the [double level osteotomy]....[but surgeons]...lacked the detailed preoperative planning associated with [this procedure] today...."
Citation: Elbardesy H, McLeod A, Ghaith HS, Hakeem S, Housden P. Outcomes of double level osteotomy for osteoarthritic knees with severe varus deformity. A systematic review. SICOT J. 2022;8:7. doi: 10.1051/sicotj/2022009. Epub 2022 Apr 1. PMID: 35363133; PMCID: PMC8973300.
-
Quote from peer-reviewed paper:
"...The main advantage [of double level osteotomy] is to maintain a horizontal joint line and avoid creating secondary anatomic deformities...."
Citation: Sautet P, Kley K, Khakha R, Ollivier M. Minimally Invasive Double Level Osteotomy in Severe Knee Varus: Pearls and Pitfalls. Arthrosc Tech. 2022 Jun 21;11(6):e1105-e1109. doi: 10.1016/j.eats.2022.02.023. PMID: 35782831; PMCID: PMC9244850.
How is a double-level osteotomy performed?
On the operating table a closing-wedge distal femoral osteotomy is performed first, under X-ray control, using K-wires to define the intended cuts.
A retractor is used to protect protect the nerves and blood vessels in this area. Once the defined bone wedge has been removed and the bony defect fixed closed with a plate and screws, then the opening-wedge high tibial osteotomy is performed. The wedge is held open with spreaders and a donor bone wedge is pushed in to fill the opening, and again the new position is held in place with a plate and screws.
Forum discussions
- Femoral Osteotomy and Tibial Osteotomy??
Patients discuss this difficult decision of an osteotomy both above and below the knee.
 2018 -
2018 -