FEATURED TECHNOLOGY
The Regenerative Clinic
✐ Surgeon: Tendinopathy: causes and treatments explained
✐ Surgeon: The Regenerative Clinic: Platelet Rich Plasma injections for Tennis elbow (elbow tendinopathy)
✐ Surgeons: Dr. Mikel Sánchez speaks to The Regenerative Clinic about using PRP in Sports Medicine
PRP is an abbreviation for 'Platelet Rich Plasma', a concentration of platelets separated from a blood sample by centrifuge.
 Page updated February 2024 by Dr Sheila Strover (Clinical Editor)
Page updated February 2024 by Dr Sheila Strover (Clinical Editor)
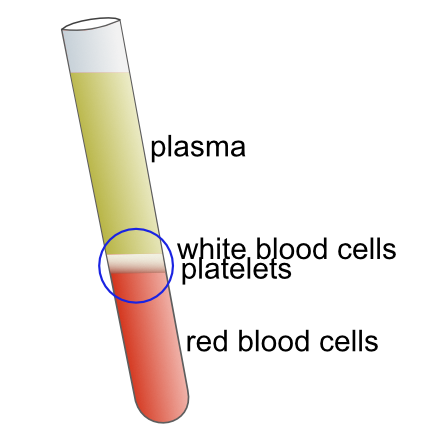
Illustration to show the separation of the platelet and white blood cell layers from a sample of blood which has been centrifuged.
This layer of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) can be separated from the rest of the sample and the components will still be active.
What is PRP used for?
Platelets are cellular fragments that break off from large cells in bone marrow and are released into the blood, where they enhance and regulate healing by the production of special growth factors.
By centrifuging a patient's own blood, the fresh platelets can be separated out into 'platelet-rich-plasma' (PRP) and injected back into ligaments and other soft tissues in the same patient in the hope that healing will be enhanced and speeded up.
Because the material is the patient's own, there will be no issue of incompatibility or rejection.
-
Quote from peer-reviewed paper:
"...Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is a simple, efficient, and minimally invasive method of obtaining a natural concentration of....[the patient's own Growth Factors which have the]....ability to modulate or augment the healing process and expedite recovery times...."
Citation: Cole BJ, Seroyer ST, Filardo G, Bajaj S, Fortier LA. Platelet-rich plasma: where are we now and where are we going? Sports Health. 2010 May;2(3):203-10. doi: 10.1177/1941738110366385. PMID: 23015939; PMCID: PMC3445108.
PRP use in cartilage damage and early osteoarthritis
Once joint cartilage it damaged, it is hard for it to recover. Joint cartilage has no nerves or blood vessels, and is dependant for its nutrition on being bathed with joint fluid which is less nourishing than blood.
Then the cartilage cells themselves are limited in their ability to multiply, differentiate and move into the damaged area.
So modern surgical techniques rely on releasing stem cells into the area by poking holes into the underlying bone marrow, and transferring healthier cartilage from an undamaged area into a damaged one, or by multiplying the cells in a laboratory, perhaps on a matrix, and transplanting them back into the damaged area.
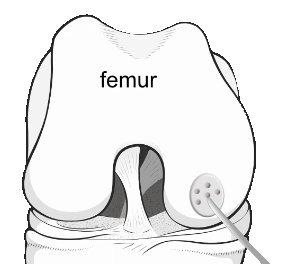
Illustration of microfracture
PRP may be used as an adjunct to such procedures, and can be prepared in the operating room.
-
Quote from peer-reviewed paper:
"....PRP has become a popular adjunct to other cartilage repair methods as it contains an array of anti-inflammatory substances and growth factors...."
Citation: Liang Y, Li J, Wang Y, He J, Chen L, Chu J, Wu H. Platelet Rich Plasma in the Repair of Articular Cartilage Injury: A Narrative Review. Cartilage. 2022 Jul-Sep;13(3):19476035221118419. doi: 10.1177/19476035221118419. PMID: 36086807; PMCID: PMC9465610.
PRP use in ligament and tendon injuries
Surgeons may inject PRP into healing tendons and ligaments.
-
Quote:
"...Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) may affect soft tissue healing via growth factors released after platelet degranulation....The literature is replete with studies on the basic science....[but]....well-controlled human studies are lacking."
Citation: Cole BJ, Seroyer ST, Filardo G, Bajaj S, Fortier LA. Platelet-rich plasma: where are we now and where are we going? Sports Health. 2010 May;2(3):203-10. doi: 10.1177/1941738110366385. PMID: 23015939; PMCID: PMC3445108.
-
Quote:
"....PRP is safe and may be efficacious....[but the]....greatest limiting factor for PRP is the lack of standardization....In addition to platelets, PRP contains varying levels of....[white blood cells (WBCs)]....that may either positively or negatively affect the repair process. The decision to include or exclude WBCs in PRP application is a major point of controversy...."
Citation: Chen X, Jones IA, Park C, Vangsness CT Jr. The Efficacy of Platelet-Rich Plasma on Tendon and Ligament Healing: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis With Bias Assessment. Am J Sports Med. 2018 Jul;46(8):2020-2032. doi: 10.1177/0363546517743746. Epub 2017 Dec 21. PMID: 29268037; PMCID: PMC6339617.
