Osteochondritis dissecans is a destructive condition of bone, where blood supply becomes insufficient to a small section of cartilage and its underlying cartilage.
 Page updated March 2024 by Dr Sheila Strover (Clinical Editor)
Page updated March 2024 by Dr Sheila Strover (Clinical Editor)
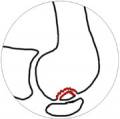
What is the cause of osteochondritis dissecans?
There is to date no proof of a single cause for osteochondritis dissecans, and it is likely that many different factors are involved.
Certainly it is associated with children, and small traumas to the knee are likely to be a factor, but the condition is also seen in adults.
-
Quote from peer-reviewed paper:
"....OCD remains an etiological, histological, and therapeutic mystery"....[There are] "4 different possible causes; traumatic, ischemic, hereditary, and idiopathic....Repetitive stress to immature knees and on the tibial spine on the lateral aspect of the medial femoral condyle during internal rotation of the tibia may contribute....Poor vascularity and induced ischemia have been described as a potential cause....[and]....cases of identical twins presenting with a similar disease process are highly suggestive of a genetic component"
Citation: Bruns J, Werner M, Habermann C. Osteochondritis Dissecans: Etiology, Pathology, and Imaging with a Special Focus on the Knee Joint. Cartilage. 2018 Oct;9(4):346-362. doi: 10.1177/1947603517715736. Epub 2017 Jun 22. PMID: 28639852; PMCID: PMC6139592.
-
Quote from peer-reviewed paper:
"....rare in patients who are <10 or ≥50 years old...Boys have more risk....Participation in high-level athletics is associated with the development of OCD...."
Citation: Chau MM, Klimstra MA, Wise KL, Ellermann JM, Tóth F, Carlson CS, Nelson BJ, Tompkins MA. Osteochondritis Dissecans: Current Understanding of Epidemiology, Etiology, Management, and Outcomes. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2021 Jun 16;103(12):1132-1151. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.20.01399. PMID: 34109940; PMCID: PMC8272630.
How is osteochondritis dissecans diagnosed?
Patients may complain of knee pain and swelling, with noises in the knee (crepitus or clicks) and there may be episodes of knee locking due to loose bodies in the knee. The quads muscles may be weak on that side, although this, too, is non-specific.
Diagnosis is usually confirmed by X-rays and MRI scan.
-
Quote from peer-reviewed paper:
"....This lesion is best observed in lateral and axial radiographic views, and it is located distally and preferentially in the medial facet(20). Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are important for defining the location, extent and viability of the lesion....."
Citation: Mestriner LA. OSTEOCHONDRITIS DISSECANS OF THE KNEE: DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT. Rev Bras Ortop. 2015 Nov 4;47(5):553-62. doi: 10.1016/S2255-4971(15)30003-3. PMID: 27047865; PMCID: PMC4799442.
How is osteochondritis dissecans managed?
If the fragment dies (osteonecrosis), then the area is managed like a chondral defect. The area is cleaned out and a cartilage repair technique such as ACI or OATS may be employed to repair the area.
-
Quote from peer-reviewed paper:
"....The options vary according to whether the lesions are stable, unstable, viable or unviable....."
Citation: Mestriner LA. OSTEOCHONDRITIS DISSECANS OF THE KNEE: DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT. Rev Bras Ortop. 2015 Nov 4;47(5):553-62. doi: 10.1016/S2255-4971(15)30003-3. PMID: 27047865; PMCID: PMC4799442.
Forum discussions
- "OCD (Osteochondritis Dissecans) Spreading?"
Story of a patient with progressive OCD.
Relevant material -
 2012 - Case presentation of OCD treated with microdrilling and PRP - by Professor Adrian Wilson (Knee Surgeon)
2012 - Case presentation of OCD treated with microdrilling and PRP - by Professor Adrian Wilson (Knee Surgeon)