This is a review article discussing the significance of prevention and early recognition of arthrofibrosis. The authors note that arthrofibrosis of the knee can be localised or global, and can restrict flexion or extension of the knee or movement of the patellofemoral joint. They stress that rehabilitation of arthrofibrosis of the knee is amongst the toughest challenges in orthopaedics.
Prevention and Early Detection of knee arthrofibrosis after ACL surgery
Because arthrofibrosis is so difficult to treat, they stress that prevention is the best approach and especially preventing prolonged immobilisation, infection or poor positioning of an anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) graft. With respect to ACL injuries they stress that -
- surgery should be avoided if the knee lacks full ROM
- placement of the graft in the right position needs to be meticulous
- bleeding after surgery needs to be avoided
- rehabilitation needs to be early and appropriate
The authors stress that once arthrofibrosis has developed it needs to be recognised early and treated appropriately. After any knee surgery, but especially after cruciate surgery, it is important to closely monitor knee motion, to identify early motion problems, and also to monitor pain which may be indicative of tissue tethering.
Monitoring the patient with suspected arthrofibrosis
Surgical Management of established knee arthrofibrosis
The authors point out that details of the specific surgical procedures for arthrofibrosis have already been published by others, and briefly outline that where surgery is necessary they manage to treat most of their patients with arthroscopic rather than open surgery.
Arthroscopic surgery concentrates on -
- re-establishing the suprapatellar pouch
- releasing the medial and lateral retinacula
- maintaining the pre-tibial recess
- inspecting the notch for impingement
For open surgery they have a 9-step procedure where each of these areas above is systematically examined and any adhesions or scarring are freed. In addition attention is paid to inspecting the posterior capsule and releasing any adhesions around the -
- tibial insertion of posterior capsule
- femoral insertion of posterior
and doing a lateral capsulotomy (cutting the capsule itself) if needed.
They stress that surgery should be followed by an appropriate rehabilitation and pain management protocol.
The Role of Manipulation
The authors suggest that manipulation can play a role, but generally they advocate that it is best to relieve the adhesions surgically, as this is more precise and causes less damage and bleeding than manipulation. They suggest that manipulation may have a role before the immature scar tissue stiffens up - about 3-4 months after the initiating insult - but they themselves they rarely use isolated manipulation once the knee is chronically stiff as this can lead to joint surface damage and even bone breaks. Even if used earlier it should be used with caution as the quads muscle can tear (leading to muscle inflammation - 'myositis') or even rupture.
They do note that other authors have apparently used manipulation more freely than they themselves would advocate.
Pain killers and anti-inflammatories
Pain control after surgery is considered to be essential, and may include opioids by mouth or injection, and in many cases an indwelling epidural for several days after surgery. Anti-inflammatories are general advocated - usually NSAIDS but occasionally intravenous steroids.
Rehabilitation
The authors stress that early motion and weight bearing are essential in -
- post ACL surgery
- post arthrofibrosis surgery
There is some variation between individuals but they feel that the normal ROM is -
- Normal extension is hyperextension - % degrees in males and 6 degrees in females
- Normal flexion is 140 degrees in men and 143 degrees in women
When not to be aggressive
The authors particularly advocate caution when -
- the knee is hot
- reflex sympathetic dystrophy is suspected
- myositis is suspected (calcification can be seen in the muscles on X-ray)
Key resource -
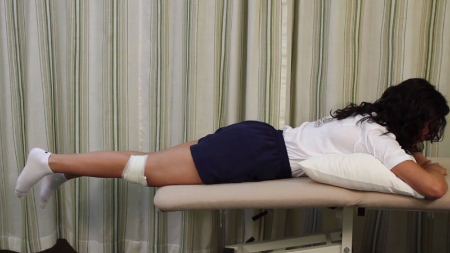
Prone heel hangs - the difference in height between the two heels can be recorded and monitored to give a quick idea of improvement or deterioration in extension.
