Pes planus is the same as flat foot.
 Page updated April 2024 by Dr Sheila Strover (Clinical Editor)
Page updated April 2024 by Dr Sheila Strover (Clinical Editor)
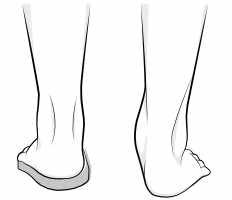
Illustration showing foot before and after orthotic correction.
Relationship between flat feet and knee symptoms
The feet always need to be assessed during an evaluation of the knee.
With flat feet (pes planus or foot pronation), the lower leg is forced into internal rotation, and the stress is relayed to the knee and the kneecap.
-
Quote from peer-reviewed paper:
"...among older adults, planus foot morphology is associated with a moderately increased prevalence of frequent knee pain and medial tibiofemoral cartilage damage...."
Citation: Gross KD, Felson DT, Niu J, Hunter DJ, Guermazi A, Roemer FW, Dufour AB, Gensure RH, Hannan MT. Association of flat feet with knee pain and cartilage damage in older adults. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2011 Jul;63(7):937-44. doi: 10.1002/acr.20431. PMID: 21717597; PMCID: PMC3087845.
Orthotics and pes planus
A visit to an orthotist should determine whether a corrective shoe insert is likely to help with any secondary knee symptoms.
-
Quote from peer-reviewed paper:
"....Pes planus is a physical problem and the arch height of each individual is different....."
Citation: Açak M. The effects of individually designed insoles on pes planus treatment. Sci Rep. 2020 Nov 12;10(1):19715. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-76767-y. PMID: 33184442; PMCID: PMC7665030.
-
Quote from peer-reviewed paper:
"....the mechanical consequences of flat feet are often correctable using foot orthoses....."
Citation: Gross KD, Felson DT, Niu J, Hunter DJ, Guermazi A, Roemer FW, Dufour AB, Gensure RH, Hannan MT. Association of flat feet with knee pain and cartilage damage in older adults. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2011 Jul;63(7):937-44. doi: 10.1002/acr.20431. PMID: 21717597; PMCID: PMC3087845.