A meniscal cyst is a fluid-filled tender lump at the joint line of the knee, arising from the meniscus shock absorber.
 Page updated February 2024 by Dr Sheila Strover (Clinical Editor)
Page updated February 2024 by Dr Sheila Strover (Clinical Editor)
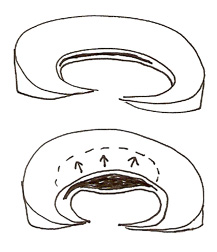
With walking, the clam-like split may allow fluid to enter, but a valve-action hinders it from leaving. Fluid pressure builds up inside the cavity.
Eventually the fluid pushes out the outer rim of the meniscus.
How does a meniscal cyst form?
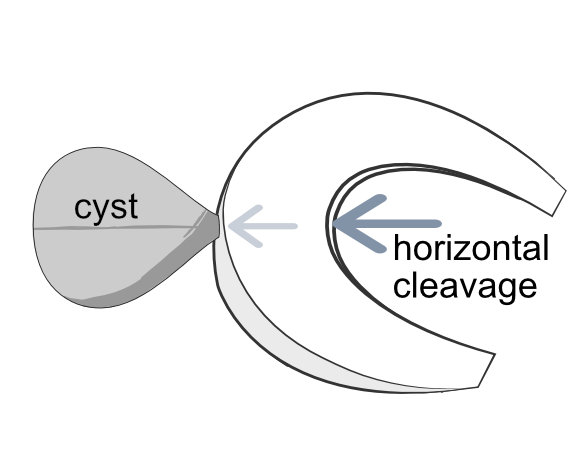
A meniscal cyst starts with a horizontal cleavage tear, perhaps from a twisting injury. The sliding motion of the upper and lower part of the meniscus can trap fluid in the cleavage, and then the lip can close like a clam so that pressure of the fluid inside the cleavage forces a passage through to the outside of the meniscus.
How to diagnose a meniscal cyst
Meniscal cysts are more frequent on the lateral side of the knee, often in association with a horizontal tear of the meniscus. External rotation of the tibia may cause the lateral mass to become more prominent, while internal rotation of the tibia may cause the mass to completely disappear. Ultrasound may be useful in establishing the presence of fluid in the lump, and the diagnosis can be confirmed with MRI.
Recurrent meniscal cyst
Even after surgery a meniscal cyst may reoccur.
-
Quote from peer-reviewed paper:
"Various theories for the recurrence of meniscal cysts even after arthroscopic surgery have been provided including inadequate debridement, poor disruption of the “check-valve mechanism”, as well as a concomitant large meniscal tear that may hinder a surgeon’s ability to adequately debride the cyst and the connecting tract"
Citation: Haratian A, Bolia IK, Hasan LK, Fathi A, Solaru S, Homere A, Petrigliano FA, Weber AE. Arthroscopic Management of Meniscal Cysts: A Systematic Review. Orthop Res Rev. 2021 Sep 17;13:123-139. doi: 10.2147/ORR.S321893. PMID: 34557043; PMCID: PMC8455512.
Forum discussions
- numbness over most of knee Post Op ?normal
Patient discussing issues after meniscal cyst surgery.